Patient experience (Janice):

First symptoms or without treatment: “[By the time I was diagnosed,] the symptoms had progressed to a very obvious uncontrollable movement, … back and neck pain … Then the pain got worse from the constant muscle spasms, so it got really bad.”
Reappearance of symptoms between treatment injections can take a toll on you physically. When benefits from treatment wear off before the next injection, people with CD have reported disruptions in their ability to work, interact socially, drive, and even perform simple activities of daily living.
Are you experiencing the signs and symptoms of cervical dystonia?
Cervical dystonia, also called spasmodic torticollis, occurs when nerve signals tell the neck muscles to tighten or spasm. This can cause your head to shake or twist in a different direction. You may also feel severe pain and discomfort. The contractions may be continuous or occur as spasms. In some people, symptoms may seem to go away but are often recurring.
In adults with CD, the abnormal position of the head may vary, depending on the muscles that are affected, as shown below:
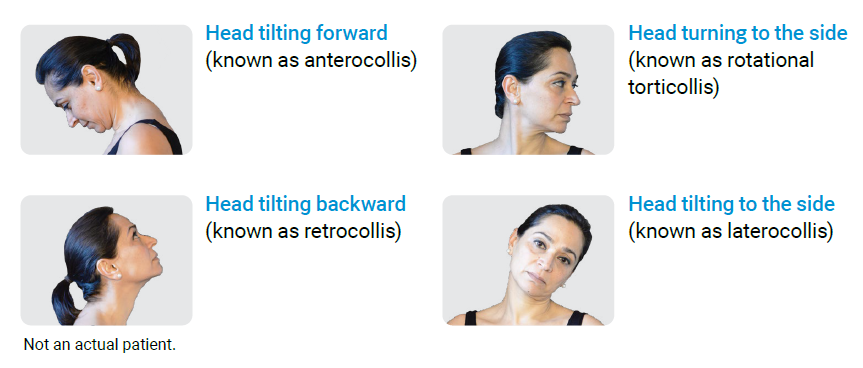
The most common form of CD is rotational torticollis, but it is common to have a combination of different position types.
Don’t wait to talk to your doctor
Be sure to tell your doctor about all the symptoms you’ve been having, including:
- Continuous contractions or sudden spasms
- Abnormal neck and head positioning
- Pain and difficulty doing activities you were able to do before
It’s important to discuss your symptoms with your doctor, whether or not you are currently experiencing them.
Doctor Discussion Guide

This guide will help you think through your treatment goals and, with your doctor’s help, decide if Dysport may be right for you or your loved one.
Signs & Symptoms
What causes cervical dystonia?
There is no known cause of cervical dystonia (CD), but there may be a genetic component and some people with CD have family members who also have the condition. CD occurs when nerve signals in the brain tell the muscles in your neck to tighten or spasm. Sometimes, CD may develop after a head, neck, or shoulder injury.

Causes of CD
Management of Cervical Dystonia
There is no cure for cervical dystonia (CD). In some people, signs and symptoms may disappear without treatment, but recurrence is common. Treatment focuses on relieving the muscle spasms and symptoms of abnormal head position and neck pain.
Treatment with Dysport
- One of these treatments for CD is Dysport, one of the botulinum toxins available.
- Dysport is a type of medicine that is injected directly into affected muscles by a specialist. It helps to temporarily block signals from the brain that tell the affected muscles to contract or tighten, usually for months at a time.
- Response to treatment may be different for each patient, so be sure to talk to your doctor regularly during treatment.
- Talk to your doctor about your condition and whether Dysport may be an option.
Dysport significantly improved abnormal head position and neck pain
In 2 clinical studies, Dysport significantly improved abnormal position of the head and reduced neck pain at week 4. Most patients did not need additional treatment until 14 weeks, and about 25% were able to wait until 18 weeks.
Based on studies of patients with CD, at least 12 weeks should pass between treatments with a botulinum toxin
Most common side effects of Dysport in adults with cervical dystonia include:
muscle weakness, difficulty swallowing, dry mouth, injection site discomfort, tiredness, headache, muscle pain, problems speaking, injection site pain, and eye problems.
Managing CD
Learn more about Cervical Dystonia
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
What is the most important safety information I should know about Dysport?
Dysport may cause serious side effects, including problems breathing or swallowing and/or spread of toxin effects, that can be life threatening and death can happen as a complication. These problems can happen within hours, or days to weeks after an injection of Dysport.
- Problems swallowing, breathing, or speaking. Treatment with Dysport can result in swallowing or breathing problems. People with pre-existing swallowing or breathing problems may be at greater risk following treatment with Dysport. Swallowing problems may last for several weeks; you may need a feeding tube to receive food or water. If swallowing problems are severe, food or liquids may go into your lungs.
- Spread of toxin effects. The effects of botulinum toxin may affect areas of the body away from the injection site and cause symptoms of a serious condition called botulism which include: loss of strength and muscle weakness all over the body, double or blurred vision, and drooping eyelids, hoarseness or change or loss of voice, trouble saying words clearly, loss of bladder control, and trouble breathing or swallowing. The risk of these symptoms is probably greatest in children treated for spasticity. These problems could make it unsafe for you to drive a car, operate machinery, or do other dangerous activities.
Call your doctor or get medical help right away if you experience these problems after treatment with Dysport.
Do not receive a Dysport injection if: you are allergic to Dysport or any of its ingredients, or cow’s milk protein; you had an allergic reaction to any other botulinum toxin product, such as Myobloc®, Botox®, or Xeomin®; or you have a skin infection at the planned injection site.
Before you receive a Dysport injection tell your doctor:
- About all your medical conditions, including if you have a disease that affects your muscles and nerves (such as ALS or Lou Gehrig’s disease [amyotrophic lateral sclerosis], myasthenia gravis, or Lambert-Eaton syndrome). You may be at increased risk of serious side effects, including difficulty swallowing or breathing.
- If you have or have had any of the following: a side effect from any botulinum toxin in the past; problems with breathing such as asthma or emphysema; swallowing; bleeding; diabetes; and slow heartbeat, or problems with your heart rate or rhythm.
- If you have plans to have surgery, had surgery on your face, have weakness of your forehead muscles (trouble raising your eyebrows), drooping eyelids, or any other change in the way your face normally looks.
- If you are pregnant or breastfeeding or plan to become pregnant or breastfeed. It is not known if Dysport can harm your unborn baby or if it passes into breast milk.
- About all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Using Dysport with certain other medicines may cause serious side effects. Do not start any new medicines until you have told your doctor that you have received Dysport in the past.
Especially tell your doctor if you have received any other injections of botulinum toxin in the last four months or ever; Myobloc®, Botox®, or Xeomin® (exactly which ones); an antibiotic recently by injection; or if you take muscle relaxants; allergy, cold or sleep medicine.
Most Common Side effects of Dysport in:
- adults with lower limb spasticity include: fall, muscle weakness, pain in your arms or legs.
- adults with upper limb spasticity include: muscle weakness.
- children (2 to 17 years of age) with upper limb spasticity include: upper respiratory infection and sore throat.
- children (2 to 17 years of age) with lower limb spasticity include: upper respiratory infection, stuffy or runny nose and sore throat, cough, and fever.
- adults with cervical dystonia include: muscle weakness, difficulty swallowing, dry mouth, injection site discomfort, tiredness, headache, muscle pain, problems speaking, injection site pain and eye problems.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of Dysport. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist. You may report side effects to the FDA at www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
What is Dysport?
Dysport is a prescription medicine that is injected into muscles and used to treat:
- increased muscle stiffness in patients 2 years of age and older with upper and lower limb spasticity
- cervical dystonia (CD) in adults
Please see full Prescribing Information including Medication Guide with Important Warning.
Botox, Xeomin, and Myobloc are registered trademarks of their respective owners.

